Food security is a key challenge on a planet with a population of over 7 billion people. According to the United Nations, the world’s population will reach 9 billion people by 2050. As a result, there will be more people to feed and fewer available resources. Food security is a worldwide problem that impacts everyone on the planet. According to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, 815 million people are chronically malnourished, and nearly a billion have micronutrient deficiencies. India currently has the world’s highest population of malnourished people, at roughly 195 million. In India, about 47 million children, or 4 out of 10 youngsters, do not reach their full individual development due to chronic malnutrition or stunting.
Food security refers to the availability of food that satisfies people’s dietary demands and food choices in order to live a healthy and active lifestyle. Food security is a wide concept that can be defined in a variety of ways. It is determined by the number of people who have adequate food to live a healthy and active lifestyle. “Having physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs for a healthy and active lifestyle at all times,” according to the United Nations. It is a measurement of our ability to generate enough food for everyone on the planet. Food security is critical because it ensures that people have access to food and can afford to purchase it. It also ensures that enough food is available for the populace and that it is safe to eat.
The three main components of food security are availability, access, and stability.
Availability:
There is a supply of food to different regions or nations since food consumers outweigh producers in every country. The storage, processing, transportation, packaging, and marketing of food are all part of the food distribution process. The food-chain infrastructure and farm storage technology also impacts the amount of food wasted in the distribution process Poor transportation infrastructure can raise the cost of delivering water and fertilizer, as well as the cost of transporting food to national and international markets. Few people or households around the world are food self-sufficient all of the time.
Access:
Individual and household preferences, as well as food affordability and distribution, are all factors that influence food access. The UN Committee of Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights state that the inability to acquire available food often causes hunger and malnutrition, which is usually due to poverty. Poverty can limit access to food and make a person or family more vulnerable to price fluctuations. whether or not the household has adequate income to purchase food at current prices or enough land and other resources to cultivate its own food determines the food Acess. Households with sufficient resources can survive weather conditions and local food shortages while maintaining access to food.
Stability:
Food stability is the ability to receive food over time. Food insecurity can be periodic, seasonal, or long-term. In transitory food insecurity, food may be unavailable for a short period of time.. Natural catastrophes and drought cause crop failure and reduced food availability at the level of food production. The regular pattern of growing seasons in food production might result in seasonal food shortages.
Hermetic Storage and Food Insecurity in India.
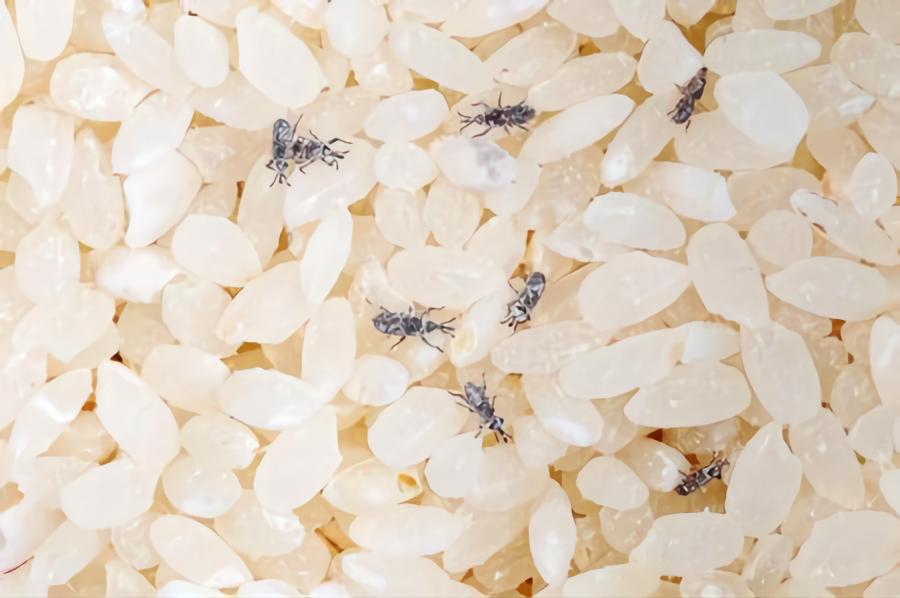
Post-harvest losses waste more than one-third of the food produced in India, contributing to food poverty. Pest infestations and inadequate storage facilities are the primary causes of these losses. Meeting food demand in a country with an ever-increasing population becomes incredibly difficult under such circumstances. Aside from the lack of food, farmers lose a lot of money when their entire crop goes to waste. Reduced post-harvest losses in India is a long-term option for enhancing the food supply. It will also contribute to the conservation of natural resources, the eradication of hunger, and the improvement of farmer livelihoods. While traditional post-harvest procedures have proven ineffectual, hermetic storage technology is gaining popularity due to its potential to prevent post-harvest losses.
How Hermetic Storage can improve food security in India.
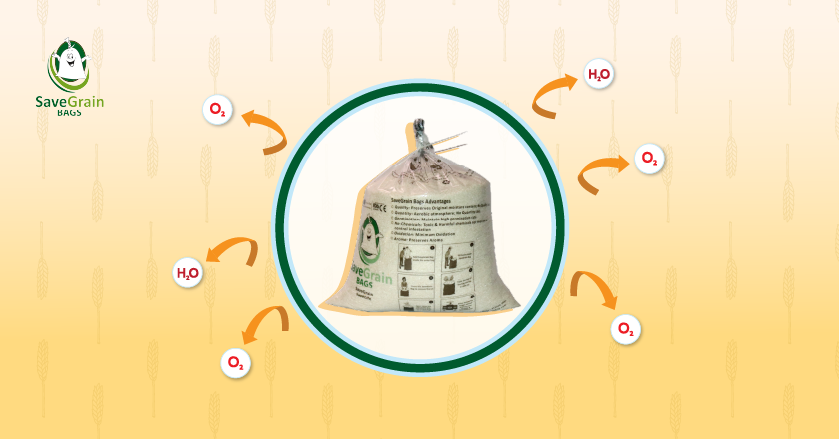
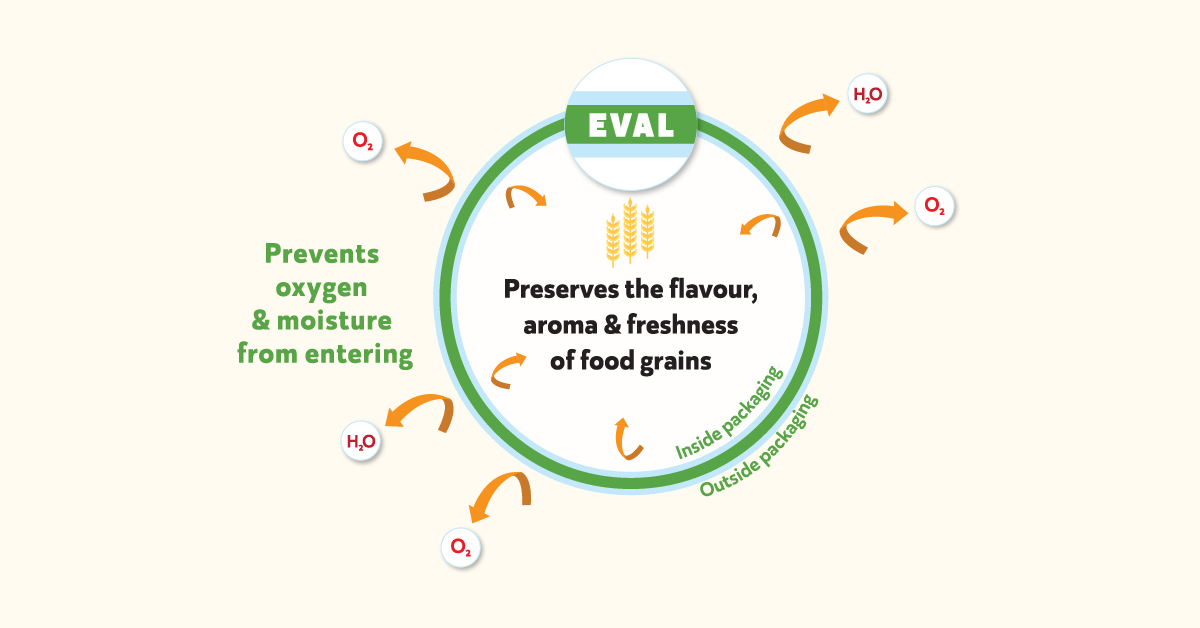
The environment is a big worry when keeping grains in India, and Hermetic Bags can help with that. They produce a controlled atmosphere with low humidity and a comfortable temperature. An air-tight technology protects the grains inside these bags, therefore the weather outside does not affect them. Hermetic bags create airtight, self-regulating, and regulated environments due to which the moisture level is still ideal. As a result, when there is a lack of moisture, the grains do not become hard. They’re also free of bug infestations and mold growth caused by excess moisture.
The hermetic bags can be used to store a variety of dry items, such as grains, cereals, lentils, pulses, and other seeds. Flour, herbs, and spices like turmeric and chilli powder can also be preserved in hermetic bags. Furthermore, in recent years, preserving coffee, cocoa beans, and tea in them has become increasingly popular. These bags can also store nuts such as cashews and peanuts. These bags are available in a variety of sizes and can be used for both commercial and home purposes.
Hermetic bags use hermetic technology to produce a controlled environment that prevents air from passing through. As a result, the temperature remains altered, and there are no bug infestations owing to a lack of oxygen.
Save Grain Bags provides hermetic storage bags that protect grain from spoiling. Between the grains and the outside environment, they serve as a moisture and air barrier. As a result, humidity, external climatic conditions, and pest infestation have no effect on your goods while it is stored in them. They are also recyclable, reusable, affordable, simple to use, and capable of storing large volumes of food grain. As a result, it’s ideal for post-harvest storage in India.